IMF more optimistic about global economy in 2024, but growth slows in eurozone

Supported by the economy of the United States and some developing countries, starting with India and Brazil, the world economy appears to be on track to perform better than expected, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimated on Tuesday, April 16, remaining cautious. by 2025.
The Washington-based institute now expects global growth of 3.2% in 2024, up slightly from its January estimate of 3.1% and at the same level for 2025, unchanged from its forecasts at the start of the year.
This is the second positive revision of the fund’s expectations, but these expected indicators of the global economy will confirm its slowdown in the long term, which is significantly below the historical trend observed between 2000 and 2019, which averaged 3.8%. And even more than the last century.
“Stable” growth in the face of inflation
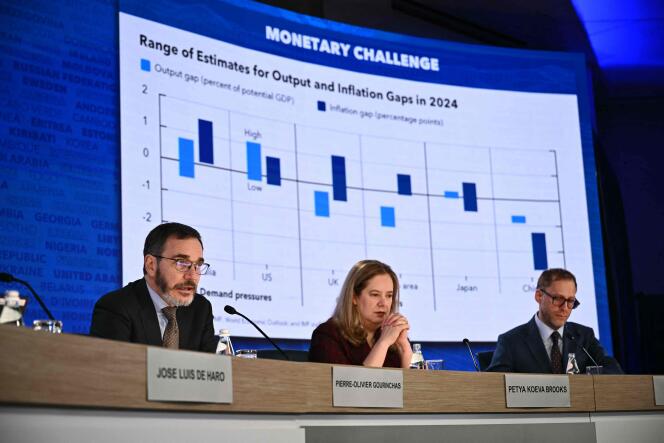
“The global economy continues to demonstrate excellent resilience, with growth remaining stable and inflation easing, but many challenges remain.”The Chief Economist of the International Monetary Fund, Pierre-Olivier Gurinchas, announced this at a press conference.
Following the publication of the first version of the World Economic Report (WEO) last October, the IMF revised its forecast for global growth to 0.3%.
Despite indicators that remain high and inflation that varies by country – close to target in Europe and below China but still very high in the United States – the strength of employment and consumption markets allows the global economy to show. some reliability.
France’s growth has been revised downwards
After a positive revision of 0.6 percentage point (pp) in January from its original October forecast, the IMF has again revised down, by the same proportion, this year’s US growth, which it now expects to see at 2.7%.
“The very solid performance of the United States is the result of its productivity, labor supply growth, but also demand, which remains strong and can lead to inflation.” This should prompt the Federal Reserve to take a cautious and gradual approach to easing. About his monetary policy, in detail Mr. Gurinchas.
A trend that, however, is not found in other advanced economies, and especially in the Eurozone, whose growth is already weak, slightly decreased to 0.8% (− 0.1 pp). This is due to the fragility of the region’s two leading economies, Germany and France, whose growth in both cases was revised downwards by 0.3 percent, 0.2% and 0.7% respectively.
“Eurozone growth will recover this year, but we are starting from very low levels”Pierre-Olivier Guerinchas recalls, “Unlike the United States, there is no sign of the economy overheating, the European Central Bank (ECB) should now be cautious about turning to monetary policy easing.”.
Italy is also expected to continue to slow, also by 0.7%, but Spain is expected to show a significantly more positive trend, by 0.4 pp to 1.9%. Outside the EU, the UK should also see its economy remain sluggish, with growth expected to be just 0.5% (−0.1 pp).
China’s economy is slowing down
As for developing countries, India and Brazil experienced the strongest upward revisions, with 6.8% and 2.2% respectively expected this year. For India, good domestic demand performance as well as a growing active population will support growth that will be among the highest in the world. As for Brazil, expected growth from 2023 remains lower, even better than initially expected, especially due to the effects of monetary tightening and ongoing fiscal consolidation.
China, on the other hand, sees its forecasts unchanged, with 4.6% growth expected this year, a sign that China’s economy is continuing to slow.
“The Chinese government last month announced measures to stimulate the economy, but weakness in the real estate sector remains persistent and our approach, given these two elements, is to leave our forecast unchanged.” For the Chinese economy, explained Mr. Gurinchas.
As in 2023, the Russian economy, on the other hand, should remain strong, with a new revision of growth, which is now expected this year at 3.2% (+0.6 pp), despite the fact that there are still economic sanctions supporting the volume of public spending, especially military spending in the war in Ukraine in context.
Source: Le Monde
Leave a Reply